Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Welcome to MGI’s guide on autoimmune diseases. These conditions can be difficult to diagnose and manage, so we’ve put together this overview to help you better understand them. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of autoimmune diseases, including what they are and how they impact the body. We’ll also provide information on some of the most common types of autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes.
If you or a loved one have been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease, it can be overwhelming to navigate the complex world of treatments and management strategies. That’s why we’ve included information on how autoimmune diseases are diagnosed and treated, as well as some self-care and coping strategies for living with these conditions.
So let’s dive in and learn more about autoimmune diseases and how to manage them.
What are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the immune system attacks healthy cells in the body, mistaking them for harmful invaders. Normally, the immune system is designed to protect the body from foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses. However, in people with autoimmune diseases, the immune system can become confused and start attacking healthy tissues and organs.
There are different types of autoimmune diseases, each affecting different parts of the body. Some common types include lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes. The exact cause of autoimmune diseases is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors that trigger the immune system to attack healthy cells.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases can affect any part of the body, and there are over 80 different types that have been identified. Here are some of the most common autoimmune diseases: lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, A chronic disease that causes inflammation and pain in various parts of the body, including the joints, skin, and internal organsMultiple Sclerosis (MS)A disease that affects the central nervous system, causing symptoms like muscle weakness, vision problems, and difficulty with coordination and balanceRheumatoid ArthritisA chronic disease that causes inflammation and pain in the joints, as well as potential damage to the bones and other tissues in the bodyType 1 DiabetesA disease that affects the pancreas and causes the immune system to attack the insulin-producing cells, leading to high blood sugar levels
Other common autoimmune diseases include psoriasis, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
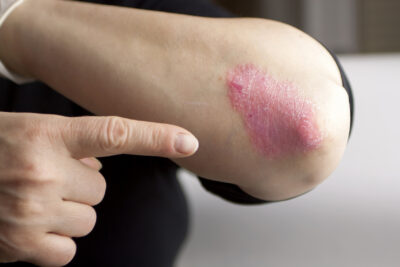
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin. It causes red, scaly patches to appear on the skin, usually on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. In some cases, psoriasis can also affect the joints, leading to a form of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease that affects the small intestine. It occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the intestine in response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This can cause a range of symptoms, including diarrhea, bloating, and weight loss.
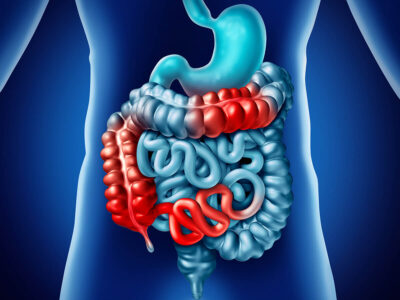
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refers to a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary depending on the specific condition and the organs affected. However, there are some common signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin rashes
- Digestive issues
- Swelling of glands
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
It is worth noting that many of these symptoms are non-specific and can be attributed to other medical conditions, making diagnosis of autoimmune diseases particularly challenging. As a result, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
In some cases, autoimmune diseases can also cause more serious complications, depending on the organs and tissues that are affected. For example, autoimmune diseases affecting the heart can cause heart failure, while those affecting the kidneys can lead to kidney failure.
Overall, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of autoimmune diseases and to seek medical attention if you experience any of them. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Causes of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While the exact cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, researchers believe that a mix of these factors can trigger the immune system to attack healthy cells in the body.
Genetic Factors
Research has shown that some autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and multiple sclerosis, are more prevalent in certain families. While having a family member with an autoimmune disease does not guarantee that you will develop the condition, it does increase your risk. Certain genes have been linked to autoimmune diseases, but having these genes does not necessarily mean that you will develop the condition.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers are external factors that can trigger an autoimmune response in people who are genetically predisposed to the condition. These triggers include viral and bacterial infections, as well as exposure to toxins and chemicals. Some common environmental triggers include cigarette smoke, stress, and certain medications.
Infection
Autoimmune diseases have also been linked to certain infections, such as strep throat and Lyme disease. In some cases, the immune system can mistakenly attack healthy cells in the body after fighting off an infection. This can lead to the development of an autoimmune disease.
Stress
While stress is a normal part of life, chronic stress can lead to a weakened immune system. This can increase the risk of developing an autoimmune disease. Stress can also trigger inflammation in the body, which can worsen symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
Overall, the causes of autoimmune diseases are complex and can vary depending on the individual. More research is needed to fully understand the factors that contribute to the development of these conditions.
Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases
Diagnosing an autoimmune disease can be challenging, as symptoms can be vague and overlap with other conditions. However, an accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of the disease.
Doctors will typically begin the diagnosis process by taking a medical history and conducting a physical exam. They may also order blood tests to look for specific antibodies that indicate an autoimmune disease is present. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may also be used to examine the affected parts of the body.
However, because symptoms can be so varied, it may take time and multiple tests to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis. It’s important to work closely with your doctor and to communicate all of your symptoms, no matter how small, to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of autoimmune diseases
The Mind-Gut-Immunity Clinic (MGI Clinic) was the brain-child of Dr. Dasari, who himself struggled with auto-immune and digestive dysfunction. He envisioned a reliable team of doctors who critically analyze conditions and put patients’ needs first. The methods outlined in our protocols are based on top-reviewed academic papers from leading research universities and scientific journals.
The MGI Clinic Method provides:
- Clear, actionable information, powered by the latest research.
- Easy to miss strategies for turning “OFF” bad genes and avoiding epigenetic triggers.
- A useful tool for tracking progress, and identifying root causes of disease.
- A reliable plan for reversing inflammation in weeks.
- A long-term solution for reversing illness permanently.
Some lifestyle changes can also help manage the symptoms of autoimmune diseases. These include:
- Getting enough rest
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding triggers that may exacerbate symptoms
Managing Autoimmune Diseases
Living with an autoimmune disease can be challenging, but there are strategies you can use to manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Below are some tips to help you take control of your health and wellbeing.
2. Practice Self-Care
Self-care is an essential part of managing autoimmune diseases. It involves taking steps to promote physical, emotional, and mental health. Some self-care strategies include:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Getting enough sleep
- Avoiding stress
- Engaging in relaxation activities such as meditation and yoga
3. Look After Your Mental Health
Living with an autoimmune disease can be stressful, and stress can worsen symptoms. It’s important to look after your mental health by:
- Talking to a therapist or counselor
- Making time for activities you enjoy
- Avoiding negative self-talk
- Practicing relaxation techniques
Remember, every person with an autoimmune disease is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Symptoms that do not resolve, can change or worsen over time. Save time, save sanity with the Mind-Gut-Immunity Clinic approach to treating conditions correctly. Doctors can miss important details impacting your recovery. The Mind-Gut-Immunity Clinic performs an extensive, independent review of each case.
Frequently Asked Questions about Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are a complex and often misunderstood set of conditions. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about autoimmune diseases:
How common are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases affect millions of people around the world, with some estimates suggesting that as many as 50 million Americans have an autoimmune condition. Certain autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, affect women more frequently than men.
Can autoimmune diseases be cured?
Currently, there is no known cure for autoimmune diseases. However, with proper management and treatment, many people with autoimmune conditions are able to lead full and active lives. See how MGI Clinic can help you today HERE.
Is it possible to prevent autoimmune diseases?
While there is no surefire way to prevent autoimmune diseases, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These may include maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine, reducing stress, and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins.